Hello Everyone Welcome Back To LearnEverytime.com This is Gautam, And in this post we are going to Learn about Interface in Java in Details or Depth, and also Doubt Questions we will see.
Interface Definition:
- An interface in Java is a blueprint of a class. It has static constants and abstract methods.
- The interface in Java is a mechanism to achieve abstraction. There can be only abstract methods in the Java interface, not method body. It is used to achieve abstraction and multiple inheritance in Java.
- In other words, you can say that interfaces can have abstract methods and variables. It cannot have a method body.
Before Going Depth in Interface We must Know Why we use Interface in Java?
There are mainly three reasons to use interface. They are given below.
- It is used to achieve abstraction.
- By interface, we can support the functionality of multiple inheritance.
- It can be used to achieve loose coupling.
Declaration Of Interface:
Syntax:-
★ Internal addition by the compiler:
The Java compiler adds public and abstract keywords before the interface method. Moreover, it adds public, static and final keywords before data members
In other words, Interface fields are public, static and final by default, and the methods are public and abstract.

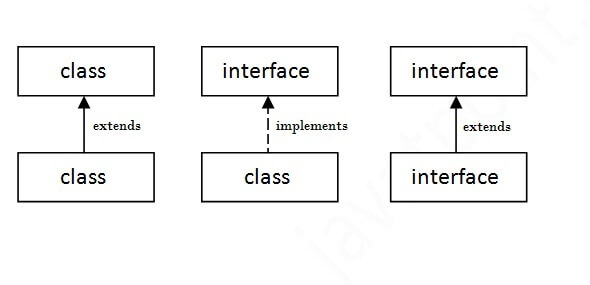
⭐ The relationship between classes and interfaces
As shown in the figure given below, a class extends another class, an interface extends another interface, but a class implements an interface.
⭐ Java Interface Example
In this example, the Printable interface has only one method, and its implementation is provided in the Inter1 class.
Output:
Hello
Let's see another example of java interface which provides the implementation of Bank interface.
File: TestInterface2.java
Output:
ROI: 12.77
✸ Multiple inheritance in Java by interface
If a class implements multiple interfaces, or an interface extends multiple interfaces, it is known as multiple inheritance.

Example Programs:
Output:
Hello Welcome
Q) Multiple inheritance is not supported through class in java, but it is possible by an interface, why?
Ans--> Multiple inheritance is not supported in the case of class because of ambiguity. However, it is supported in case of an interface because there is no ambiguity. It is because its implementation is provided by the implementation class.
Social media link: Click Here
THANKS FOR VISITING THIS BLOG PAGE 💖.

0 Comments